NYISO’s Comprehensive Reliability Plan Identifies Future Challenges to Grid Reliability

The System and Resource Planning Department at the New York Independent System Operator (NYISO) recently completed our 2023-2032 Comprehensive Reliability Plan (CRP), which analyzes the electric system on a ten year time horizon for reliability risks and investment needs to keep the electric system reliable.
The CRP, issued biennially, highlights growing risks to electric system reliability, including:
- projected increases in peak demand due to electrification of the transportation and building sectors
- additional generator deactivations
- delayed implementation of planned infrastructure projects
- and extreme weather
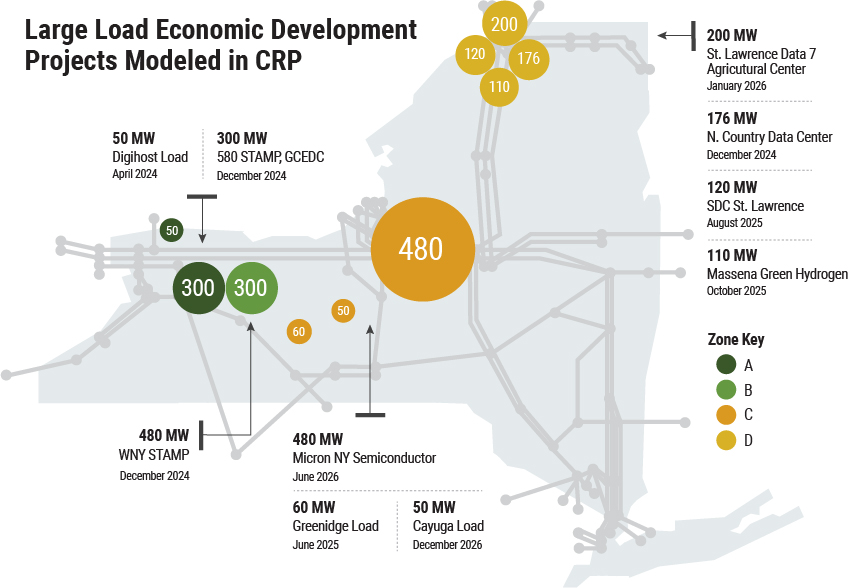
In addition to rising demand due to continued electrification, several large commercial projects in upstate New York are in development and are forecasted to significantly increase energy use over the planning period. We took a closer look at this development in another recent blog post.
Further, state legislation enacted last year will require the phase-out of the New York Power Authority’s small natural gas plants located in New York City by December 31, 2030. If demand on the grid grows at a rate greater than the buildout of new generation and transmission, reliability deficiencies could arise within the CRP’s ten-year planning period.
The CRP highlight how potential reliability risks may be resolved by new capacity resources coming into service. Construction of additional transmission facilities, increased energy efficiency, integration of distributed energy resources and/or growth in demand response participation can also alleviate risks and resource needs.
“Our latest report demonstrates the continued importance of the NYISO’s in-depth planning process and the need to closely monitor the rapidly changing electric grid,” said Zach Smith, Senior Vice President, System and Resource Planning.
The plan underscores the importance of the timely completion of planned transmission projects ― primarily the Champlain Hudson Power Express (CHPE) project ― to maintain system reliability. Without the CHPE project in service by May 2026 or other offsetting solutions, reliability margins within New York City would be deficient beginning in 2026.
Transition from a summer peaking system to a winter peaking system also poses challenges to grid reliability, according to our CRP. This shift, driven by the electrification of the building and transportation sectors, is forecasted to occur within ten years. A winter peaking system introduces new reliability concerns, particularly around fuel availability for gas-fired generators. Based on a recent assessment of New York’s fuel and energy security, the CRP states the following:
Preliminary results of the 2023 Fuel and Energy Security study demonstrate that NYISO will need to rely significantly on dual-fuel generation resources to support winter system reliability into the next decade and changes to the resource mix may complicate system operations during multi-day cold snap conditions. The frequency and severity of projected potential loss of load events grow over the modeling time horizon as the generation mix evolves and the demand for electricity increases.
Given the rapid pace of change on the bulk electric system, the NYISO will continue to monitor these and other developments to determine whether changing system resources and conditions could impact the reliability of the New York electric grid.
The competitive wholesale electricity markets administered by the NYISO are an essential tool to mitigate risks on the electric system, as well as facilitate the transition of the grid to increased renewables and decarbonization as required under state law. The competitive markets continue to evolve and adapt to guide and attract new market entry and retention of resources that support reliability.
