NYISO’s Comprehensive Reliability Plan Identifies Future Challenges to Grid Reliability
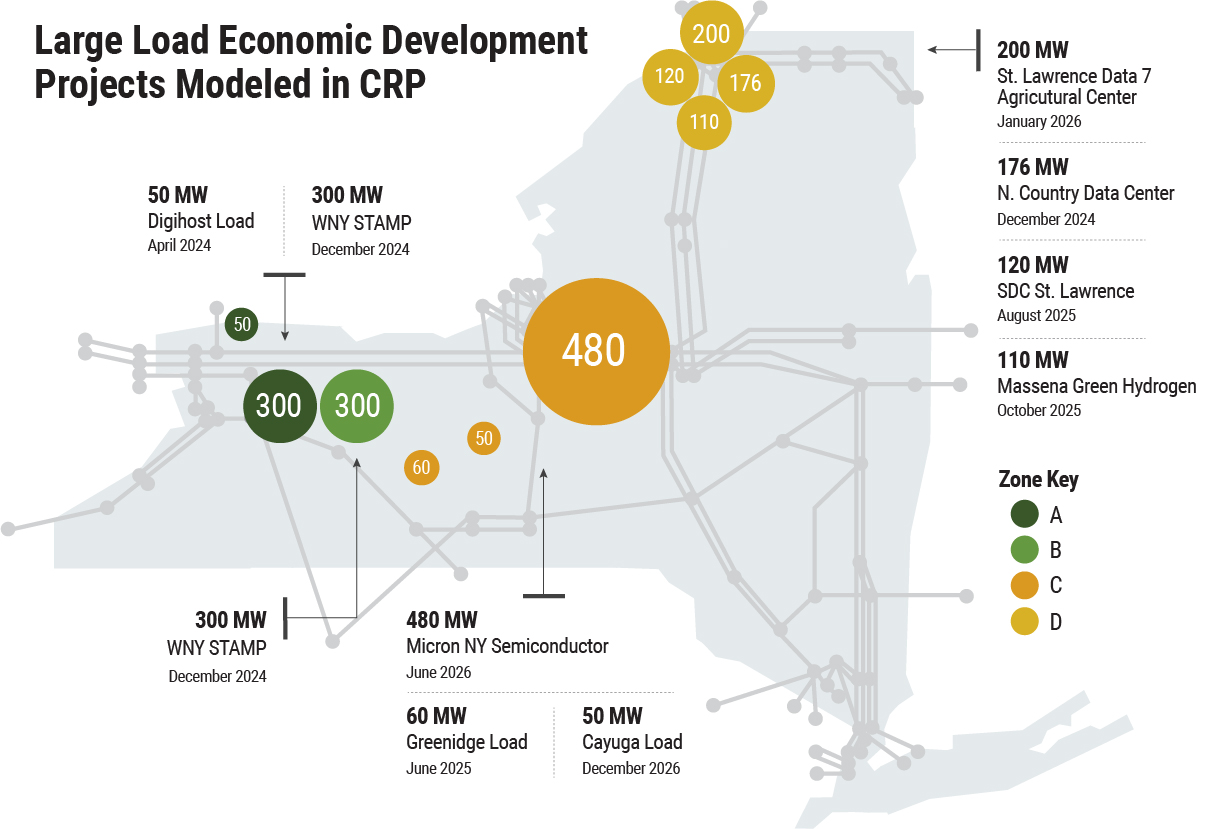
The System and Resource Planning Department at the New York Independent System Operator (NYISO) recently completed our 2023-2032 Comprehensive Reliability Plan (CRP), which analyzes the electric system on a ten year time horizon for reliability risks and investment needs to keep the electric system reliable.